Ocular Drug Delivery Systems
Drug formulated eye drops make up 90% of ophthalmic medications. However, barriers in the eye - such as blinking, tears, and the blood retina barrier - reduce permeability, with only about 5% of the drug entering the posterior segment. [3]
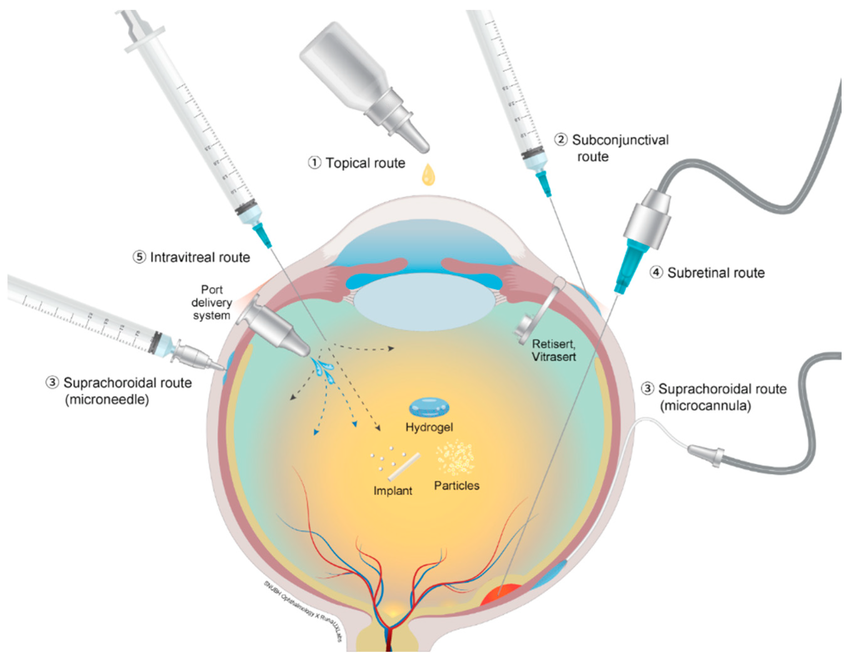
Delivering medicine to the eye remains one of the greatest challenges in ophthalmology. Existing routes of medication administration to the posterior segment — where the primary vascular structures of the eye are — either lack sufficient bioavalibility and delivery of the drug of interest (i.e. topical solutions such as eye drops) or are too invasive and bring discomfort to the patients’ treatment experience (i.e. intravitreal and suprachoroidal injection).
Routes of ocular drug administration [4].Our biomaterials lab is developing advanced drug delivery solutions that offer an alternative to existing drug delivery methods - including hydrogels, microneedles, and nanoparticles - to ultimately overcome these barriers in ocular medication administration. We combine advanced in vitro and in vivo testing strategies, along with the development of artificial microfluidic eye models to replicate the complex ocular environment.
Recent Publications
Rudeen, K. M., Maloney, C. M., Lydon, K. L., Teixeria, L. B. C., Mieler, W. F., & Kang-Mieler, J. J. (2025). Treatment Efficacy of a Dual Release of Aflibercept and Dexamethasone From a Single Hydrogel Drug Delivery System in a Rodent Model. Translational Vision Science & Technology, 14(6), 31. https://doi.org/10.1167/tvst.14.6.31
Story, B. D., Park, S., Roszak, K., Shim, J., Motta, M., Ferneding, M., Rudeen, K. M., Blandino, A., Ardon, M., Le, S., Leandro, Yiu, G., Mieler, W. F., Thomasy, S. M., & Kang-Mieler, J. J. (2025). Safety and biocompatibility of a novel biodegradable aflibercept-drug delivery system in rhesus macaques. Drug Delivery, 32(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2025.2460671
[3]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33719019/
[4]https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/13/1/108